Tutorial 1: Global simulation
This is a step-by-step tutorial how to create a mesh for a global simulation and run a forward simulation.
The following instructions assume that you have installed SPECFEM3D_GLOBE and familiarized yourself with how you will run the package based on your computer configuration, as detailed in the SPECFEM3D_GLOBE User manual (Chapter 2 provides installation help). Please make sure you have the package installed on your system.
The example is distributed with the package under the EXAMPLES/ directory. However, you might need to edit these example scripts slightly to launch them on your system.
Global simulation
This is a step-by-step tutorial how to create a mesh for a global simulation and run a single forward simulation.
Setting up example folder for simulations
We will set up the example folder for simulation runs:
* databases directory: create a directory DATABASES_MPI/ into which you will put the mesh partitions:
[]$ cd SPECFEM3D_GLOBE/EXAMPLES/global_s362ani/ [global_s362ani]$ mkdir -p DATABASES_MPI
Make sure this folder is accessible by the compute nodes on your system. The example will search for this folder in the current example directory. Depending on your system setup, you may also create this as a symbolic link to a local scratch directory /scratch/DATABASES_MPI.
* parameter files: make sure you have the parameter files in a local directory DATA/ for the example:
[global_s362ani]$ ls -1 DATA/ Par_file CMTSOLUTION STATIONS
these files should already be provided in the example folder.
* executables: compile the executables in the root directory:
[]$ cd SPECFEM3D_GLOBE/ [SPECFEM3D_GLOBE]$ make
this assumes that you run the configuration beforehand by ./configure (see the manual for further configuration options). In case the compilation was successful, it will create the main executables xmeshfem3D and xspecfem3D in the bin/ directory
create a local directory bin/ to link the executables from the root directory:
[]$ cd SPECFEM3D_GLOBE/EXAMPLES/global_s362ani [global_s362ani]$ mkdir -p bin [global_s362ani]$ cd bin/ [bin]$ ln -s ../../bin/xmeshfem3D [bin]$ ln -s ../../bin/xspecfem3D
All these steps and the following mesher and solver runs are put in a process.sh bash script file in the example folder. You can simply run the script:
[global_s362ani]$ ./process.sh
to do the setup and following steps for you. The script uses a PBS scheduler to submit the corresponding cluster job. Please modify and adapt the script to your needs.
Meshing
You will need to create the mesh databases before you can run the solver.
1. the example will run the mesher in parallel on 150 CPUs. A script go_mesher_solver_pbs.bash is provided in this example folder to do this via a PBS job scheduler. You may adapt also one of the cluster scripts provided in the SPECFEM3D_GLOBE/UTILS/Cluster/ directory for this purpose.
Note: This example script will submit one single job script which contains both the meshing run and the forward solver run together. This is especially useful in case your DATABASES_MPI folder is only locally accessible on the cluster nodes (e.g. local scratch disk space) and allows you to run both meshing and forward simulation without the need to store all the created mesh database files in a globally accessible repository.
2. make sure, you have the parameter file Par_file in the local directory DATA/. This example will use the following parameter setup for the global simulation:
# forward or adjoint simulation SIMULATION_TYPE = 1 # 1 = forward, 2 = adjoint, 3 = both simultaneously NOISE_TOMOGRAPHY = 0 # 0 = earthquake simulation, 1/2/3 = three steps in noise simulation SAVE_FORWARD = .false. # number of chunks (1,2,3 or 6) NCHUNKS = 6 ... # number of elements at the surface along the two sides of the first chunk # (must be multiple of 16 and 8 * multiple of NPROC below) NEX_XI = 240 NEX_ETA = 240 # number of MPI processors along the two sides of the first chunk NPROC_XI = 5 NPROC_ETA = 5 ... # 3D model MODEL = s362ani ... # path to store the local database files on each node LOCAL_PATH = ./DATABASES_MPI ...
The number of spectral elements per chunk in both XI and ETA directions is 240. To obtain the shortest period resolved in the seismograms, you would determine:
shortest period ~ (256 / NEX_XI ) * 17
thus for this example, they are accurate down to approximately 18 s periods.
Once the mesher completed, check the output file OUTPUT_FILES/output_mesher.txt to see if the databases were generated successfully. The output file contains various mesh information, including the time step size used for your forward simulation:
time-stepping of the solver will be: 0.161500000000000
Forward simulation
To run a forward simulation, do the following:
1. set an earthquake source by modifying the file CMTSOLUTION in the directory DATA/. this example will use a CMT solution for a deep earthquake (647.1 km depth) which took place in Bolivia in June, 1994.
You can obtain more CMT solutions from the Global Centroid-Moment Tensor project catalog.
2. place your stations by modifying the file STATIONS in the directory DATA/. this example will use a very small subset of seismic stations in international networks IRIS/IDA (II) and IRIS/USGS (IU) as well as station PAS located in Pasadena, CA, USA.
You can obtain more station information from the International Federation of Digital Seismograph Networks (FDSN).
Please see the SPECFEM3D_GLOBE User manual for more detailed informations of how to specify the source and stations.
3. make sure, you have the parameter files in the directory DATA/. Most parameters in the Par_file should be set before running the mesher xmeshfem3D. The following parameters are important for this example forward simulation:
# forward or adjoint simulation SIMULATION_TYPE = 1 # 1 = forward, 2 = adjoint, 3 = both simultaneously NOISE_TOMOGRAPHY = 0 # 0 = earthquake simulation, 1/2/3 = three steps in noise simulation SAVE_FORWARD = .false. # number of chunks (1,2,3 or 6) NCHUNKS = 6 ... # number of MPI processors along the two sides of the first chunk NPROC_XI = 5 NPROC_ETA = 5 ... # 3D model MODEL = s362ani # parameters describing the Earth model OCEANS = .true. ELLIPTICITY = .true. TOPOGRAPHY = .true. GRAVITY = .true. ROTATION = .true. ATTENUATION = .true. # absorbing boundary conditions for a regional simulation ABSORBING_CONDITIONS = .false. # record length in minutes RECORD_LENGTH_IN_MINUTES = 15.0d0 ... # path to store the local database files on each node LOCAL_PATH = ./DATABASES_MPI ... # output format for the seismograms (one can use either or all of the three formats) OUTPUT_SEISMOS_ASCII_TEXT = .true. ...
this example will use a single job script go_mesher_solver_pbs.bash to run mesher and solver together. The solver should take about 1 hour 45 minutes to finish the simulation.
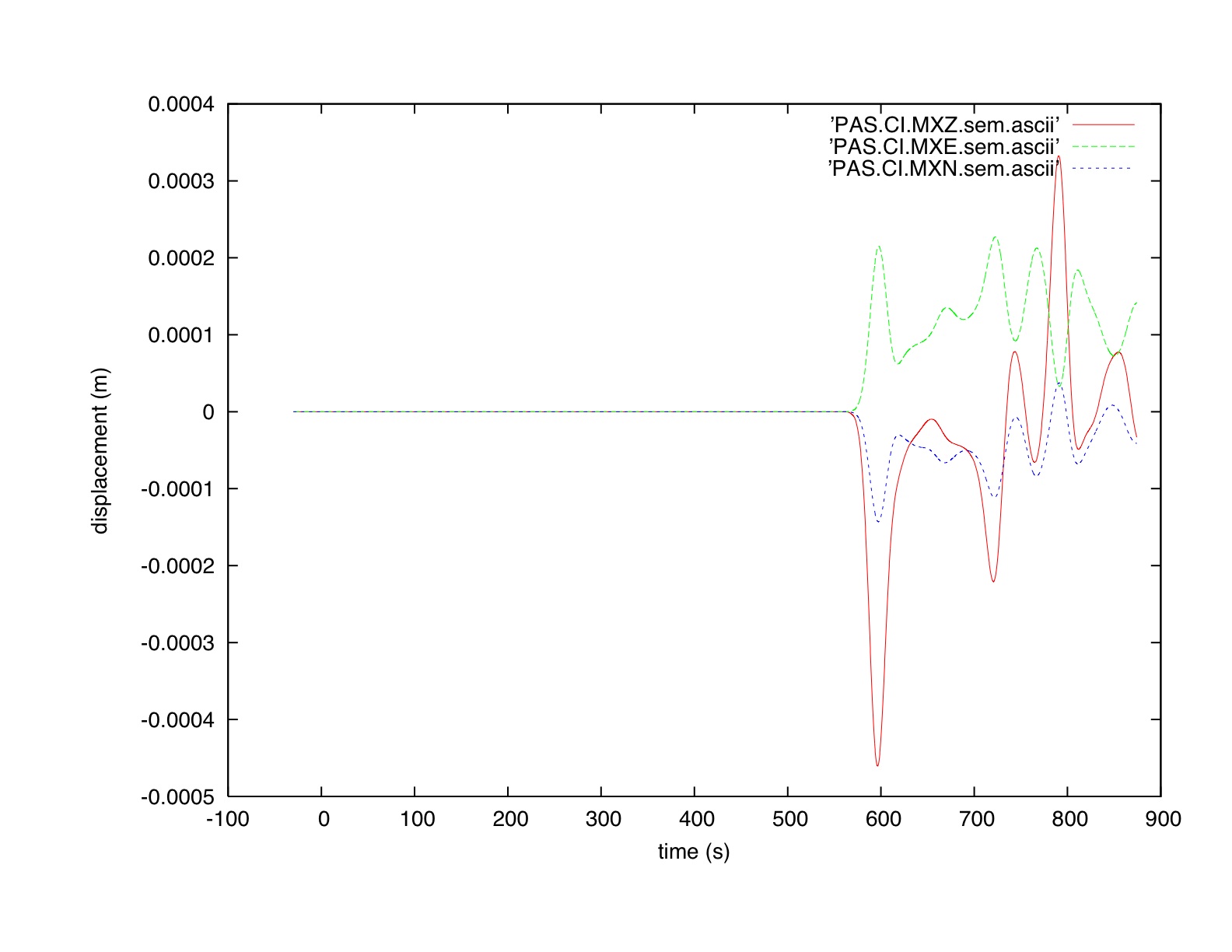
check the output file output_solver.txt in the output directory OUTPUT_FILES/ to see if the forward simulation was successfully finishing. the seismograms for station PAS should look like this, using gnuplot:
gnuplot> plot "PAS.CI.MXZ.sem.ascii" w l,"PAS.CI.MXE.sem.ascii" w l,"PAS.CI.MXN.sem.ascii" w l